Do you often wake up feeling tired even after a full night’s sleep? Do you snore loudly or frequently wake up gasping for air? These could be signs of a common sleep disorder known as sleep apnea.
Sleep apnea is a condition characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. These interruptions in breathing can occur multiple times throughout the night, leading to fragmented sleep and various health complications if left untreated.
Types of Sleep Apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common type of sleep apnea, where the airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, usually due to relaxed throat muscles.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): In CSA, the brain fails to send signals to the muscles that control breathing, resulting in pauses in breathing during sleep.
- Mixed Sleep Apnea: This is a combination of obstructive and central sleep apnea.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea:
- Loud and persistent snoring
- Pauses in breathing during sleep, often observed by a bed partner
- Gasping or choking sensations during sleep
- Daytime sleepiness and fatigue
- Morning headaches
- Irritability and mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating or remembering
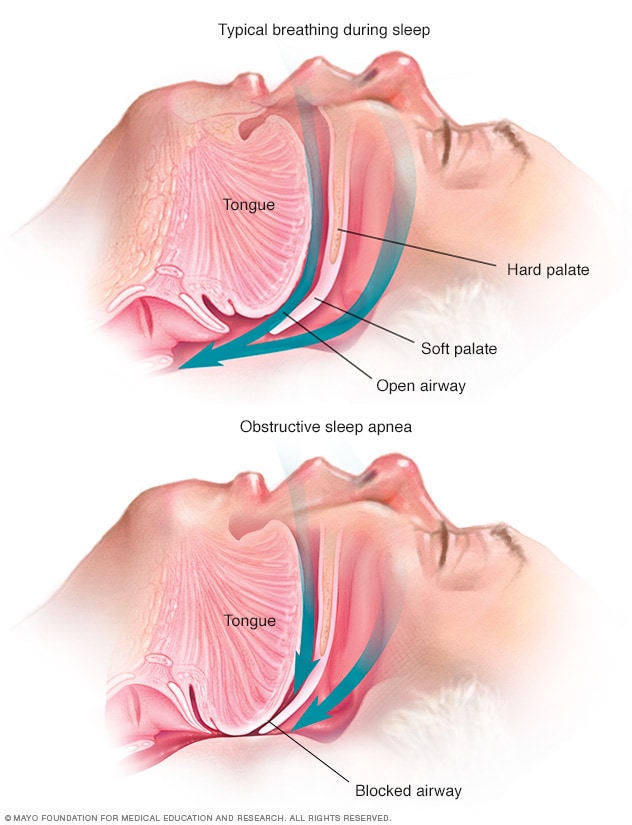
Causes of Sleep Apnea
- Obesity and excess weight, which can contribute to airway obstruction
- Narrow airways due to genetics or anatomical factors
- Aging, as muscle tone in the throat tends to decrease with age
- Smoking and alcohol consumption, which can relax throat muscles and worsen symptoms
- Family history of sleep apnea
- Certain medical conditions, such as hypertension, congestive heart failure, and diabetes
Treatment Options:
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): CPAP therapy involves wearing a mask connected to a machine that delivers a continuous flow of air, keeping the airway open during sleep.
- Oral Appliances: These devices are custom-made by a dentist and worn during sleep to reposition the jaw and tongue, helping to keep the airway open.
- Lifestyle Changes: Losing weight, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime, and sleeping on your side instead of your back can help reduce sleep apnea symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when other treatments fail, surgical procedures to widen the airway or remove obstructive tissue may be recommended.

If you suspect you or a loved one may have sleep apnea, it’s essential to seek evaluation and treatment from a qualified healthcare professional. Effective management of sleep apnea can improve sleep quality, enhance daytime functioning, and reduce the risk of associated health problems.

